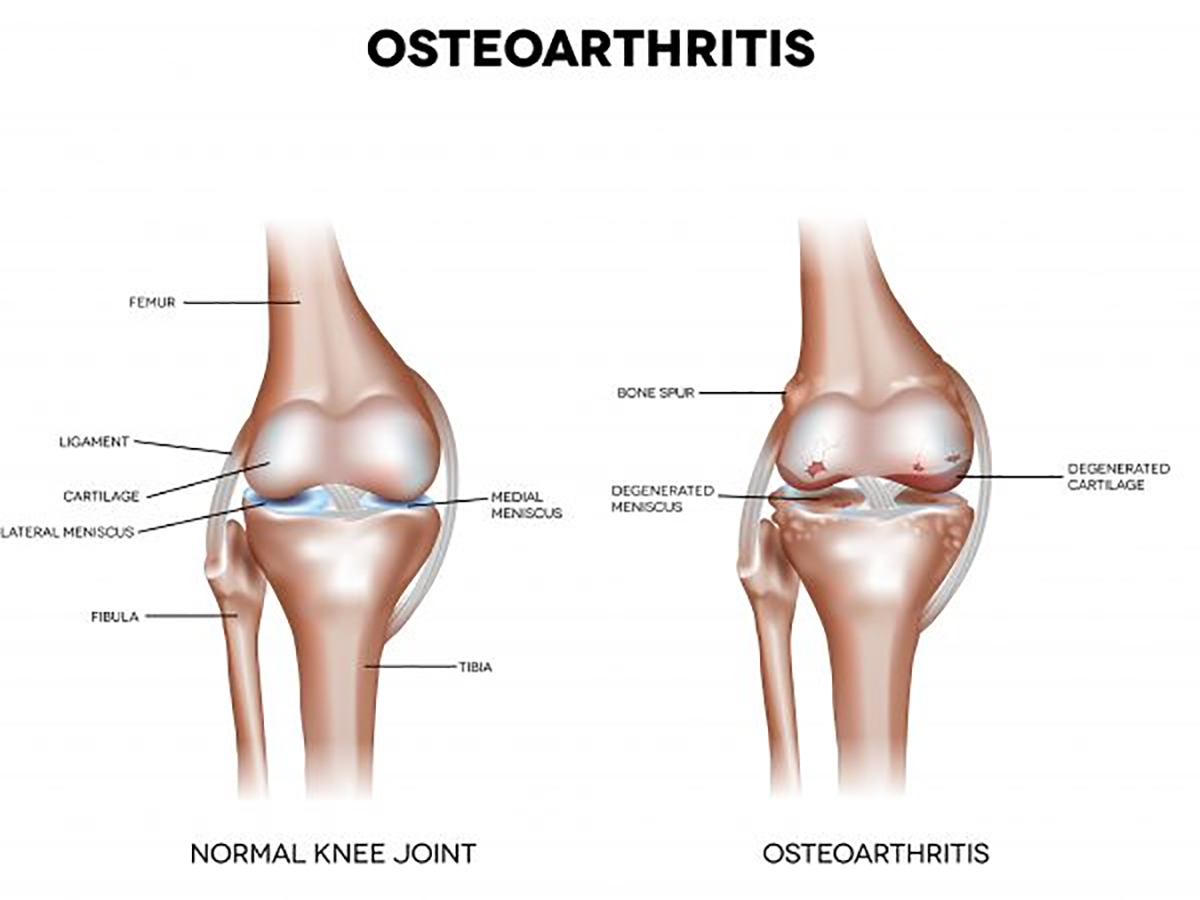
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis refers to the abnormal degeneration of the joint cartilage, exceeding the ability of repair from the body, resulting in inflammation (it means inflammation in Latin). Osteoarthritis can affect all the joints in the body and the knee joints are the most commonly affected joint, contributed largely to our genes and our lifestyles. If you have osteoporosis, it means your bones are very brittle and even a light bump or minor fall can seriously injure you.
Prevention is better than cure. Don’t let osteoarthritis fracture your future.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis often develop slowly and worsen over time, including pain (especially when climbing down the stairs), stiffness, deformity (bowed legged or knock knees) and loss of function (unable to bend fully, unable to straighten fully and unable to squat down). And once the knees become deformed, the abnormal posture of the knee will lead to accelerated damage of the joint cartilage, leading to further deformity and hence entering a vicious cycle of further destruction and deformity, resulting in intractable pain and severe loss of function of the knee joints:
- Pain – Affected joint might hurt during or after movement
- Stiffness – Joint stiffness might be most noticeable upon awakening or after being inactive
- Tenderness – Your joint might feel tender when you apply light pressure to or near it
- Loss of flexibility – You might not be able to move your joint through its full range of motion
- Grating sensation – You might feel a grating sensation when you use the joint, and you might hear popping or crackling
- Bone spurs – These extra bits of bone, which feel like hard lumps, can form around the affected joint
- Swelling – This might be caused by soft tissue inflammation around the joint.
Treatment options for Osteoarthritis
Depending on the symptoms and severity of the knee osteoarthritis, orthopedic treatment is individualized and can be divided into:
Non-operative treatments
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle strengthening, and lifestyle modification
- Anti-inflammatory medication injection (H&L)
- Hyaluronic acid injection (lubricant)
- Platelet-rich plasma injection (PRP
Surgical treatments
- Minimally invasive surgery – Arthroscopy and washout
- Open surgery – Knee replacement surgery (unicompartmental knee replacement or total knee replacement). In joint replacement surgery (arthroplasty), the orthopedic surgeon removes the damaged joint surfaces and replaces them with plastic and metal parts